Hospitals are places of healing—but what happens when the facility itself harbors a silent health risk? Mold in hospitals is a serious concern that can lead to infections, worsen respiratory conditions, and put vulnerable patients at greater risk. In the UAE, where humidity and HVAC systems often collide, mold contamination in healthcare environments is a growing challenge.
In this article, we explore the risks of hospital mold, where it tends to grow, how it can affect both patients and staff, and what professional strategies are used to detect, control, and remove it in medical settings. If you manage or work in a clinic, lab, or hospital, this guide will help you understand what to watch out for—and when to call in professional help.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Why Mold in Hospitals Is Dangerous
Unlike in homes or offices, mold in hospitals isn’t just a cosmetic or air quality issue—it can become life-threatening. Hospitals house immunocompromised patients: newborns, surgical patients, cancer patients, transplant recipients. For these individuals, exposure to mold spores—especially species like Aspergillus fumigatus or Stachybotrys chartarum (black mold)—can lead to severe lung infections, bloodstream infections, and complications.
Research has documented hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) directly linked to environmental mold exposure. Some outbreaks have been traced back to construction dust, contaminated ventilation ducts, or undetected water leaks behind walls.
Symptoms can include:
- Fever and cough that do not respond to antibiotics
- Sinus infections or bleeding nose in neutropenic patients
- Fatigue, dizziness, or unexplained headaches in staff
Because mold spores are microscopic and airborne, they can bypass filters and land in surgical wards, ICUs, or equipment storage rooms—posing a silent but severe threat.
2. Common Sources of Mold in Hospital Settings
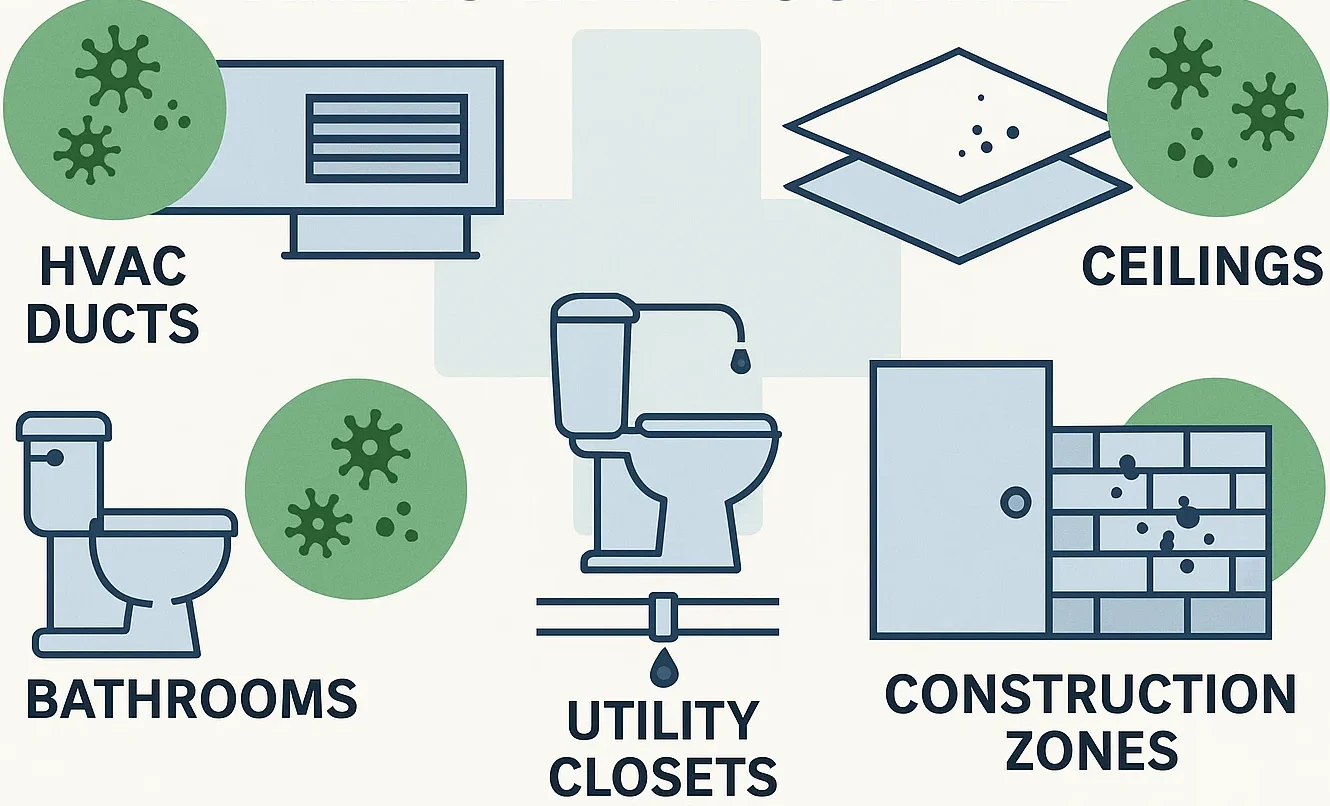
Hospitals are complex structures with many potential moisture sources. Even a small issue can lead to a large infestation if not addressed. The most common areas where mold is found in hospitals include:
- HVAC Systems – Dust and condensation inside ducts can become mold breeding grounds.
- Ceiling Panels and Wall Cavities – Water leaks from plumbing or roofing can seep in unnoticed.
- Bathrooms and Utility Rooms – Poor ventilation encourages condensation and mold growth.
- Medical Storage Areas – Warm, dark, and sometimes humid, these are ideal environments for fungi.
- Construction Zones – Renovation projects often disturb dormant spores, spreading them into active areas.
Even aggressive cleaning routines may not reach hidden areas where spores are hiding. That’s why professional mold detection using tools like air quality sampling, infrared imaging, or surface swabs is often required in medical settings.
3. Regulations and Safety Protocols for Mold in Hospitals
Globally, health authorities take mold in hospitals very seriously. The CDC, WHO, and local UAE health bodies all issue specific guidelines regarding environmental cleanliness and infection control.
While there is no unified mold-specific standard across all facilities in the UAE, here are commonly followed best practices:
- HEPA Filtration: High-efficiency particulate filters should be installed in all sensitive units (e.g., operating theatres).
- Routine HVAC Maintenance: Air handlers, vents, and ducts should be inspected and cleaned regularly.
- Moisture Control Protocols: Leak detection, dehumidifiers, and proper waterproofing are essential in both old and new buildings.
- Construction Isolation: Work zones should be sealed off and air pressure controlled to avoid cross-contamination.
- Air Quality Testing: Periodic monitoring using spore trap analysis or PCR tests should be done in ICUs and oncology wards.
Compliance with these protocols helps ensure that patients are not exposed to unnecessary environmental risks during their treatment or recovery.
4. Mold Remediation in Hospitals: What It Involves
Removing mold from a hospital isn’t the same as cleaning a bathroom wall. The process must follow strict containment, decontamination, and verification procedures to prevent any disruption to medical services or exposure to patients.
Here’s a step-by-step look at how hospital mold remediation is typically handled by licensed professionals like us:
- Initial Inspection: Visual check, thermal imaging, moisture meters, and surface sampling help define the scope of contamination.
- Containment Setup: Negative air machines, sealed barriers, and HEPA filters prevent mold spores from escaping the treatment zone.
- Demolition (if needed): Contaminated ceiling tiles, drywall, or insulation may be safely removed under controlled conditions.
- Cleaning and Treatment: Use of antimicrobial sprays, fogging, and scrubbing on hard surfaces to eliminate all traces of mold and spores.
- Post-Remediation Testing: Air and surface testing to confirm mold levels are back to safe thresholds before clearance is issued.
Depending on the size and sensitivity of the area, this process can take a few hours to several days. In critical departments, remediation may be scheduled during off-hours or in phases to minimize disruption.
5. Preventing Mold Outbreaks in UAE Medical Facilities
Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and other Emirates experience high ambient humidity—especially during summer months. Combined with chilled indoor environments and long working hours for hospital HVAC systems, this creates the perfect storm for mold outbreaks.
To prevent future issues, we recommend the following preventive measures:
- Conduct quarterly inspections using infrared cameras and moisture probes
- Maintain relative humidity indoors between 40–60% with industrial-grade dehumidifiers
- Install smart leak detectors in areas above ceiling panels and under sinks
- Train cleaning staff to recognize signs of hidden mold behind tiles or around vents
- Partner with certified mold remediation providers to handle emergencies before they spread
Hospitals should view mold not as an isolated cleaning issue—but as an infection control threat that requires proactive planning and fast response.
Conclusion
There’s no room for mold in a hospital. For patients with compromised immune systems, even a small patch can pose serious health consequences. That’s why detection, regulation, and professional remediation must be treated as core parts of facility management.
We’ve worked with clinics and care facilities across the UAE to tackle mold challenges swiftly and discreetly. If you suspect mold in any hospital environment—whether visible or hidden—click the contact button on the right-middle of this post. Let us help you restore safety and peace of mind where it matters most.













